Introduction
As we all know, the UI of the website is rendered by web browsers. And the web browsers create kinds of controls depends on the HTML code provided by the website. So, when we visit a website, the web browsers will try to get the HTML code of the website and the relative sources it needed according to Http protocol, then the browsers will create and render all the controls in this website correctly.
The View in the ASP.NET MVC determines the rendering of the website. And we can notice that the name of View is the same as Action‘s name. When an Action is executed, the ASP.NET MVC will get the View as a result by the name of the Action. Then the View will be translated into HTML code and sent to browsers as a return.
So, the rendering in the ASP.NET is about how to create the correct HTML code.
Here is the code of a simple Action.
1 | public ActionResult Index() |
In this method, it returns a ViewResult as a result. And how does it work? How does the ASP.NET find the correct view? And how to translate it into HTML code?
I will try to figure out the first question in this article (part one). And we will discuss the second question in my next blog (part two).
Details
All the source code about the ASP.NET is provided by Microsoft. And the code is posted on the Github, for more detail, visit AspNetWebStack.
Controller
The Controller class inherits the ControllerBase class. And here is the source code of the Execute method in the ControllerBase class.
1 | protected virtual void Execute(RequestContext requestContext) |
And as the code shows, when the Execute method is executed, it will call the ExecuteCore method which is an abstract method and this method is implemented in the Controller class which is the only subclass of ControllerBase.
Here is the source code of ExecuteCore in Controller class.
1 | protected override void ExecuteCore() |
It is easy to notice that there are four steps in the ExecuteCore method.
- Load temp data
- Get the name of action by the
RouteData - Call the
ActionInvoker.InvokeActionmethod to execute the action which’s name is equal to theactionName. - Save temp data
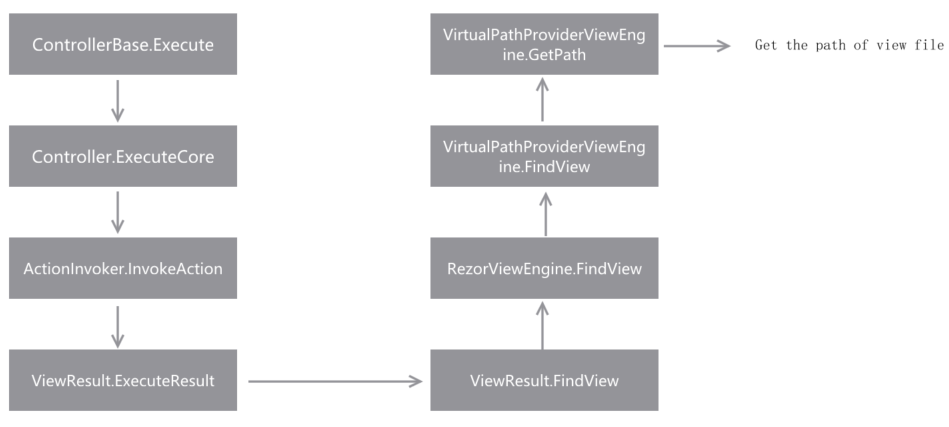
And what does ActionInvoker.InvokeAction do? How does it translate the ActionResult into the HTML code? Reading the source code with these questions, I found that in the InvokeAction method it calls ActionResult.ExecuteResult after getting the result from the action method.
1 |
|
So, I guess that the secret of how does ASP.NET translate the ActionResult into Html code is in the implementation of ActionResult class and its subclasses.
ViewResult
What does the ActionResult look like? What does the ExecuteResult method do? Let’s see the code of ActionResult class.
1 | public abstract class ActionResult |
The ActionResult is an abstract class and the ExecuteResult method is an abstract method too. Obviously, the correct implementation is in the subclass. So, I read the ExecuteResult method in the ViewResultBase class which is the base class of ViewResult and inherits the ActionResult class.
1 | public override void ExecuteResult(ControllerContext context) |
After reading this method, I am sure that this method is the core of translating the view into HTML. And there are 4 steps.
- If the
ViewNameis empty, it will set the name ofActionas view’s name. - Find the correct
Viewinstance depends on thecontext - Call the
Rendermethod of theViewinstance to write the content of theViewinto the information of theHttpContext, and then return it to the browser. - Release the
view‘s data
So, we can split the translation into two parts. The first part is to find the correct View. And the second part is to translate.
How to find the correct view
The View files are named with the name of the action method, and these files are always placed in the directory which is named with the name of the Controller class. And this directory will be placed in the View directory in the root directory.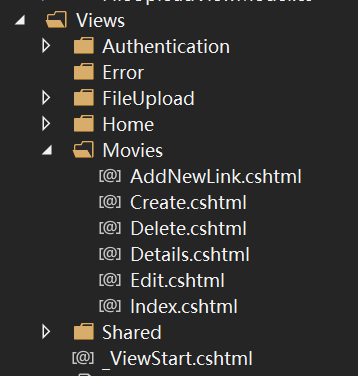
How does the ViewResult find the correct View?
Here is the source code of FindView method in the ViewResult class.
1 | protected override ViewEngineResult FindView(ControllerContext context) |
We can see from the code that the FindView method calls ViewEngineCollection.FindView method to find the View with the ViewName and MaterName. If the View is found, this method will return a ViewEngineResult instance, if not the ViewEngineResult.FindView will throw an InvalidOperationException exception.
And there are two classes we have not seen before. One is the ViewEngineCollection class and the other is the ViewEngineResult class. So, let’s continue reading the code of these classes to figure out what do they do.
ViewEngineCollection
After reading the code about ViewEngineCollection, I found that all of the instances of ViewEngineCollection are managed by a static class named ViewEngines. And the code in ViewEngines is quite simple.
1 | public static class ViewEngines |
It is easy to find that there are two special classes in the code, WebFormViewEngine and RazorViewEngine. In the MVC application, we use the RazorViewEngine class to render the View.
Here is the inheritance map of the WebFormViewEngine and the RazorViewEngine.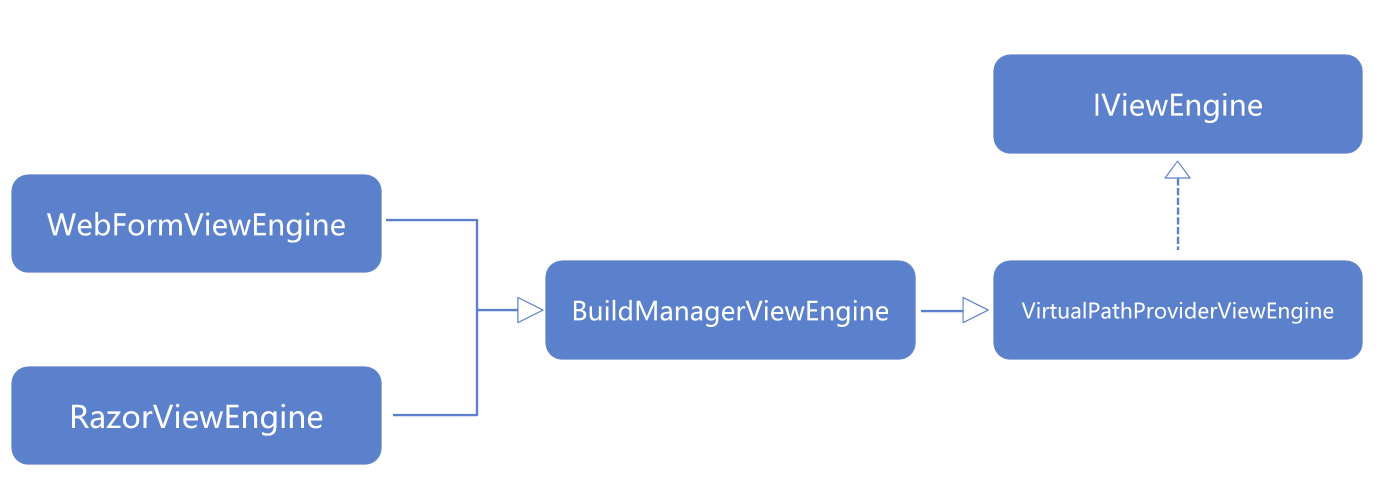
We can get some information from this picture.
- Their base class is
BuildManagerViewEngineclass, it means that these two classes are associated with building or compiling. - The base class of
BuildManagerViewEngineis theVirtualPathProviderViewEngine, it tells us that these two classes are based on the relative path to manageView.
In this article, we are talking about ASP.NET MVC. So, we ignore the WebFormViewEngine and continue reading the code of RazorViewEngine.
1 | public class RazorViewEngine : BuildManagerViewEngine |
It is important to notice that there is a magic string named ViewStartFileName, and its value is _ViewStart. So, it means the _ViewStart is the start page without changing. And we can see that the RazorViewEngine class set lots of location format strings when it is initializing, and these formats specify the search path for the pages.
Finally, I found the implementation of the FindView method in the VirtualPathProviderViewEngine class.
1 | public virtual ViewEngineResult FindView(ControllerContextcontrollerContext, string viewName, string masterName, bool useCache) |
And there are 4 steps to create an instance of the ViewEngineResult.
- Find the correct name of the controller by the
RouteData - Get the file path of the
Viewby passing theviewName,masterNameandcontrollerNameinto theGetPathmethod - Get the master’s file path by calling
GetPathmethod - New an instance of
ViewEngineResultand return it
And the GetPath method needs the LocationFormats we mentioned above to find the correct path.
Conclusion
Overall, we probably know that how does ASP.NET MVC finds the correct View file. When a Controller instance is executed, it will call ActionInvoker.InvokeAction method to execute the correct Action by the actionName. And in the ActionInvoker.InvokeAction method, it calls ActionResult.ExecuteResult method, in this method the ViewResult.FindView method is called to find the correct View. And after reading the code about RazorViewEngine and ViewEngineCollection we can know that the RazorViewEngine set lots of location formats to help the VirtualPathProviderViewnEngine.FindView method to find the correct View by relative path.